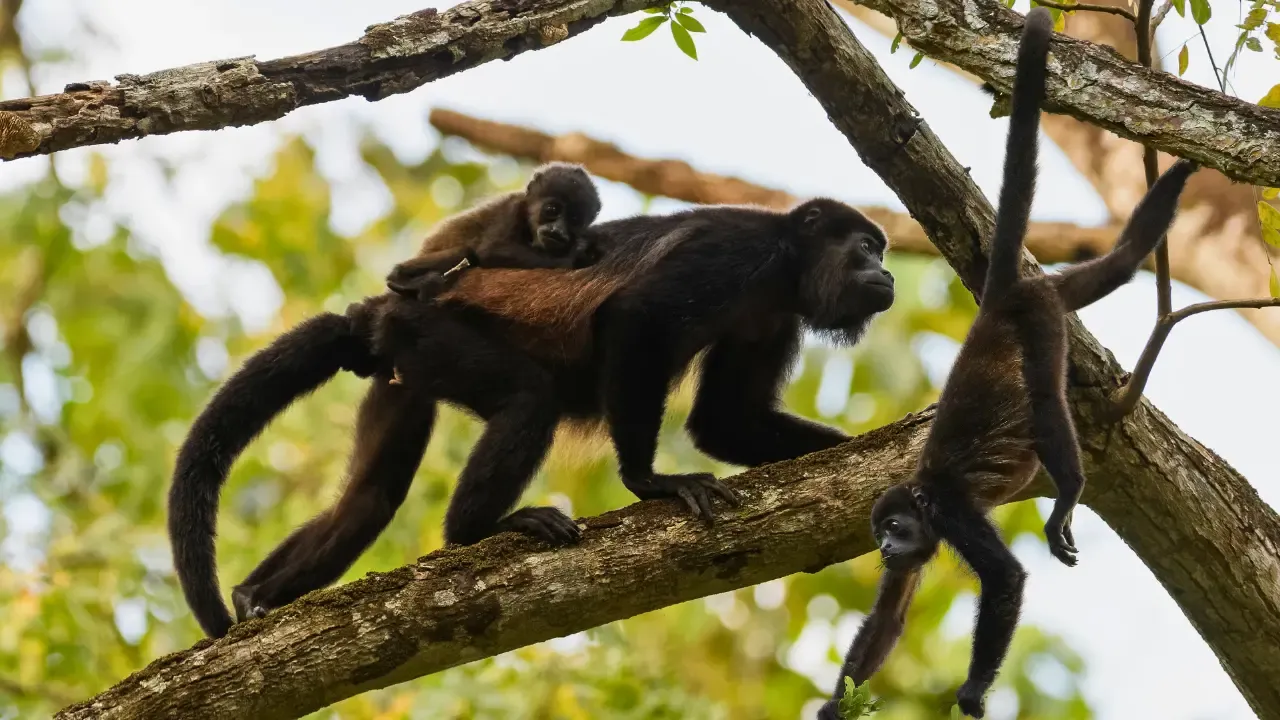
Mantled Howler Monkeys: Masters of the Canopy
The mantled howler monkey, also known as Alouatta palliata, is a species of New World monkey found in the forests of Central and South America. They are named for the thick, shaggy fur that forms a "mantle" around their necks, giving them a distinctive appearance. These monkeys are arboreal, meaning they spend most of their time in the trees, swinging from branch to branch with ease.
 |
| Mantled Howler Monkeys |
Mantled Howler Monkeys Habitat
The mantled howler monkey is primarily found in Central and South America, including countries such as Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, and Ecuador. These primates inhabit tropical rainforests, where they find an abundance of food such as leaves, fruits, and flowers. The dense foliage provides them with ample cover from predators and shelter from the elements.
They thrive in lush, humid environments where they can easily navigate their surroundings and interact with other members of their troop.
Physical Characteristics
In terms of size, the mantled howler monkey is a medium- to large-sized primate; adult males can weigh up to 9 kg, while females are smaller in size than males.
One of the most striking features of the mantled howler monkey is its thick, golden-colored mantle of fur that covers its back. This long, flowing fur gives them a regal appearance and sets them apart from other monkey species in the region. Their fur is also a dark shade of black on their face and limbs, with some individuals having a reddish tinge to their fur as well.
In addition to their luxurious fur coat, mantled howler monkeys have a robust build and prehensile tail. This long, muscular tail acts like a fifth limb, allowing the monkey to grasp and hang from branches as it moves through the forest canopy. The tail is also used for balance and coordination, helping the monkey navigate its arboreal environment with precision.
They have a large, round head with a prominent jaw and sharp teeth, which they use for feeding on leaves, fruit, and other plant matter.
Mantled Howler Monkeys Behavior
One of the most striking features of the mantled Howler monkey is their vocalizations. These primates are known for their loud, deep calls that can be heard for miles through the dense rainforest. The males of the species produce these calls to establish their territory and communicate with other members of their group. In fact, the Mantled Howler Monkey is said to have one of the loudest calls of any primate. Their calls are 25 times louder than those of similarly sized spider monkeys.
Mantled Howler Monkeys are excellent climbers and spend most of their lives in the treetops, rarely descending to the forest floor.
Mantled Howler Monkeys Social Structure
Mantled Howler Monkeys live in small social groups called troops, typically consisting of one male, several females, and their offspring. These groups can vary in size from a few individuals to dozens of monkeys, depending on the availability of resources in their habitat.
The male is the dominant member of the group and is responsible for defending the territory and mating with the females. Female Mantled Howler Monkeys have a close bond with their young and often share caregiving duties with other females in the troop. This social structure helps to maintain order within the group and ensure the survival of the species.
Mantled Howler Monkeys Diet
Mantled Howler Monkeys spend the majority of their day foraging for food on the treetops. Mantled howler monkeys are primarily herbivorous, feeding on a diet of leaves, fruits, and flowers. They have specialized stomachs with multiple chambers that allow them to digest tough, fibrous plant material. This adaptation helps them extract nutrients from their vegetarian diet and sustain their energy levels as they move through the treetops.
One interesting behavior of mantled howler monkeys is their ability to engage in "geophagy," or the consumption of soil. It is believed that this behavior helps them supplement their diet with essential minerals and nutrients that may be lacking in their plant-based diet. This unique adaptation showcases the resourcefulness of these intelligent primates.
Mantled Howler Monkeys Reproduction
Breeding in mantled howler monkeys typically occurs throughout the year, with females giving birth to a single offspring after a gestation period of around six months. The newborn monkeys are completely dependent on their mothers for care and protection, clinging to her fur as she moves through the trees. As the young monkeys grow, they will begin to explore their environment and learn essential skills from the older members of the troop.
Males in the troop may compete for the attention of females during breeding season, engaging in displays of strength and dominance to establish mating rights. Once a female has selected a mate, they will form a bond that can last for several mating seasons. This monogamous behavior helps to ensure the survival of the offspring and maintain stability within the troop.
Conservation Status
Despite their importance in the ecosystem, mantled howler monkeys are facing a number of threats to their survival, primarily due to habitat loss and fragmentation caused by deforestation and human development. The destruction of their natural habitat has led to a decline in their population numbers and an increase in human-monkey conflicts as they are forced to venture into agricultural areas in search of food.The mantled howler monkey is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN red list.
Mantled Howler Monkeys Ecological Importance
Mantled howler monkeys play a vital role in their ecosystem as seed dispersers for a variety of plant species. As they feed on fruits and leaves, they inadvertently ingest seeds that are then spread throughout the forest in their droppings. This helps to promote the growth and diversity of plant life in the rainforest and ensures the health of the ecosystem as a whole.
In addition to their role as seed dispersers, mantled howler monkeys are also prey for a number of predators in their habitat, including large birds of prey and big cats. By controlling the population of these monkeys, predators help to maintain a balance within the food chain and prevent overgrazing of vegetation in the rainforest.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mantled howler monkey is a remarkable species that serves as a symbol of the beauty and diversity of the tropical rainforests of Central and South America. From their stunning appearance to their unique behaviors and ecological importance, these primates are a marvel of nature that deserves our admiration and protection.